A Guide to Body Odor and Personal Hygiene
Body odor, or osmidrosis, is an unfortunate reality for many people and can be caused by a variety of factors. It is essential to understand the biological processes that contribute to body odor and how to maintain personal hygiene to minimize it. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the causes of body odor, the role of sweat glands, and practical tips for personal hygiene to keep you fresh and confident.
The Science of Sweat
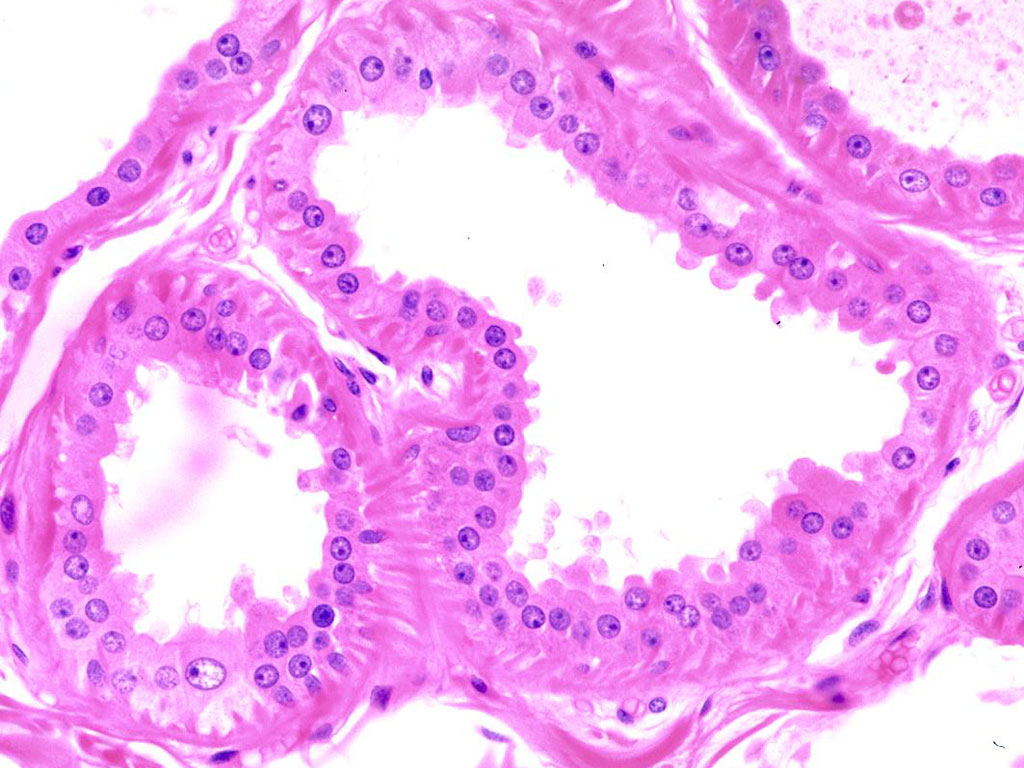
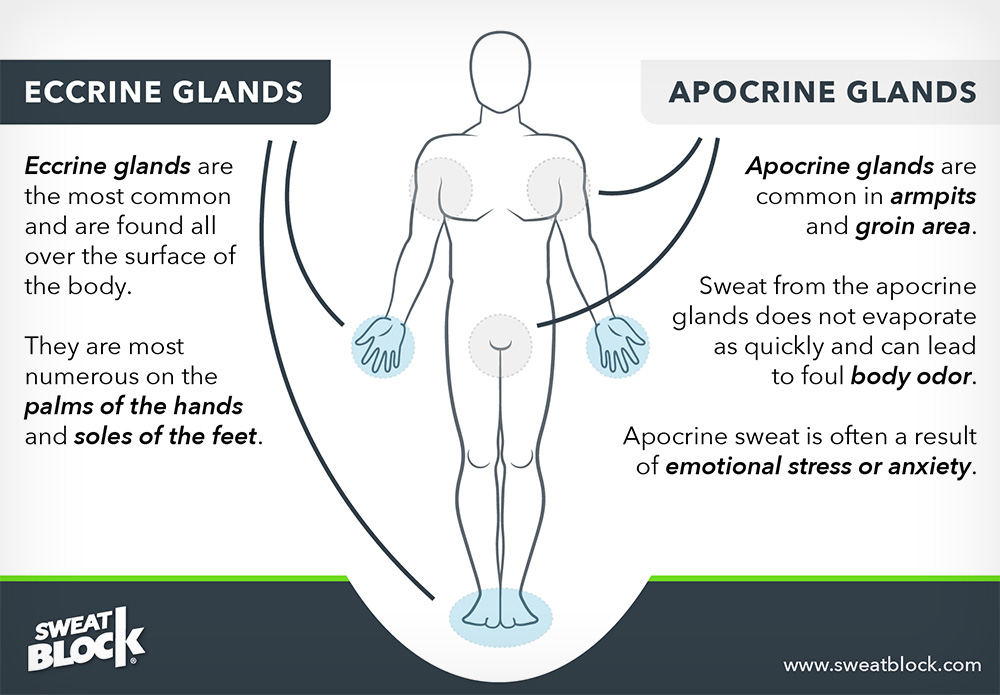
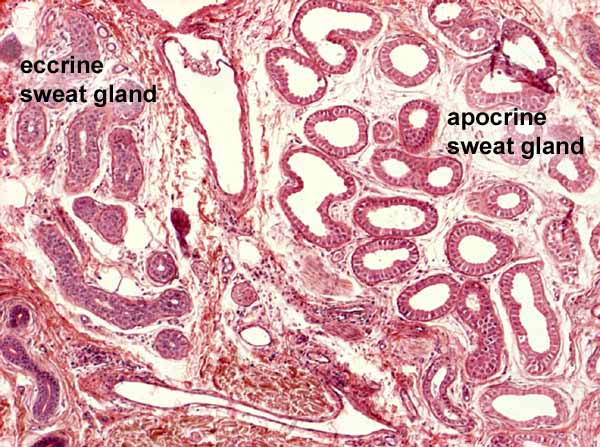
Sweat glands, known as sudoriferous glands, are responsible for producing sweat, which is a natural mechanism for cooling the body. There are two types of sweat glands: eccrine and apocrine. Eccrine glands are found all over the body and produce a watery sweat that is mostly composed of water and salts. Apocrine glands, on the other hand, are found in areas with a high concentration of hair follicles, such as the armpits and groin, and produce a sweat that contains proteins and lipids, which can contribute to body odor when they interact with bacteria on the skin.

Understanding Bacterial Breakdown
The presence of bacteria on the skin is a natural part of the human microbiome. However, when these bacteria come into contact with the sweat produced by apocrine glands, they can break down the proteins and lipids, resulting in the production of volatile sulfur compounds, which are responsible for the characteristic smell of body odor. Maintaining good personal hygiene, such as regular bathing and the use of antibacterial soaps, can help reduce the number of bacteria on the skin and, consequently, the intensity of body odor.
Strategies for Managing Body Odor
There are several strategies that can be employed to manage and reduce body odor. These include:
- Regular Bathing: Showering daily with a mild, antibacterial soap can help remove sweat and bacteria from the skin.
- Antiperspirants: Using antiperspirants can reduce the amount of sweat produced by the eccrine glands, which can help minimize the potential for odor.
- Proper Clothing: Wearing breathable fabrics, such as cotton, can help reduce the amount of moisture on the skin, making it less hospitable for bacteria to thrive.
- Diet: Consuming a diet low in odor-causing foods, such as garlic and onions, can also help reduce body odor.
Conclusion
In conclusion, body odor is a common issue that can be managed through a combination of understanding the science behind it and practicing good personal hygiene. By taking the necessary steps to reduce sweat production, minimize bacterial growth, and maintain a healthy diet, individuals can effectively manage their body odor and enjoy a more confident and comfortable lifestyle.